Subtotal $0.00
Shopping cart
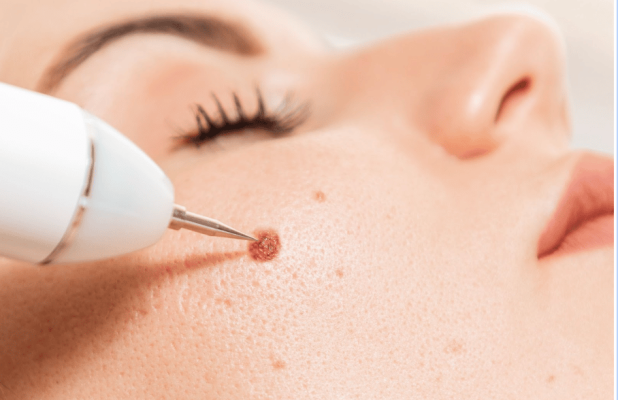
Pune’s trusted destination for advanced skin, hair & laser solutions—delivered with precision, care, and cutting-edge technology.
Camp, Pune
Let’s Stay In Touch
Subscribe for newsletter
Contact Us
+91-9359722976
Monday - Saturday